One of the most popular terms in academic, cultural, sports and business circles is the concept of coaching, which may be understood as a type of personal, group or institutional training.
Coaching as a discipline was born in the United States, in the area of sports training, with the aim of increasing an athlete’s individual performance. Since then, the practice of coaching has been extended to the most diverse fields of human activity, such as the area of human nutrition and diet, where the concept of nutritional coaching is born.
Tania Mesa – Director of Neolife Nutrition and Nursing Unit
Alejandro Monzó – Neolife Nutrition and Nursing Unit
Coaching is a transformational process whose goal is to achieve awareness, discovery, and personal and professional growth
The purpose of coaching is to improve and develop skills so that people are happier, more productive and able to achieve their goals in a balanced way. It is an interpersonal process between a tutor (coach) and a student (coachee) within a context that involves a specific action that is productive, relational, personal, and results-oriented (1). It is focused on helping the individual, engage in their own acquisition and improvement of skills that will allow them to achieve their individual and personal goals.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the prevalence of obesity nearly tripled between 1975 and 2016. Every year, 2.8 million people die from obesity or being overweight. In 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight and more than 650 million were obese (2). In 2003, the WHO stated that:
“It is not longer enough for a doctor to give information and advice to achieve long-term changes in a patient’s behavior” (3).
For a person to make a change and adopt a healthy lifestyle, it is not enough to show them what they should and shouldn’t do. For a great many people, this strategy alone is not enough. There are different therapies aimed at changing behavior, used to achieve a greater adherence from patients who want to acquire healthy eating habits and lose weight (4).
One of these is nutritional coaching, which, by definition, is a process through which the patient identifies and overcomes their own obstacles, creates the right environment and adopts the attitude and determination to achieve a change in their diet, while improving at the same time other aspects of their behavior and lifestyle (5).
During the coaching sessions, the coach talks to the coachee to identify their reality and situation, and consider the barriers that prevent them from reaching their goal. In this way, the coachee becomes the protagonist and is responsible for their decisions. No one tells them what to do. They are free to make their own decisions during the process and choose what they want to change in their habits, and, most importantly, “why” they want to do this (Table 1).
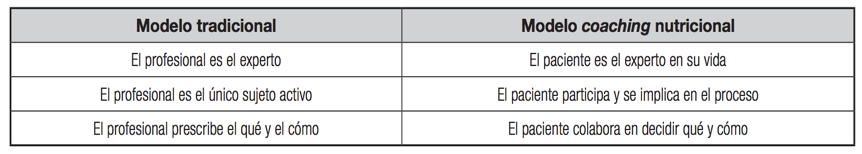
From a scientific standpoint, obesity and being overweight are considered recurrent phenomena. Relapses are very common because these problems are usually treated with dietary adjustments that do not take into account the psychological components and underlying inappropriate habits (6). In the nutritional coaching process, the following key elements stand out:
- Basic goal: weight loss and/or the acquisition of habits for a healthy life.
- Need for motivation towards change. Recognition of achievements.
- Objectives: personalized, realistic, and agreed upon.
However, a key element in any weight control process is the understanding and management of thoughts and behaviors that are associated with dietary behavior. These may interfere with weight loss, and it is precisely the analysis of thoughts and behaviors that determines the food intake that is chosen in the nutritional coaching process, which is completely different from other weight control processes (1, 5). Therefore, the nutritional coaching process will identify behaviors and/or beliefs that may be interfering with the person’s efforts to lose weight, such as eating with no limits after exercise, using food to cope with stress, feeling that dessert is a must after meals, etc.
During the coaching process, the coach creates a safe environment, in which there is no prejudice, allowing the exploration of the coachee’s objectives through active listening and the use of open-ended questions. The coach takes into account (1, 4):
- Patient empowerment. The ability to make decisions based on your values and take responsibility for taking care of yourself. To empower yourself, it’s important to remember past triumphs.
- Patient-centered interventions. You are the protagonist because you are the expert in your life.
- Collaboration. It’s a joint effort.
- An adult relationship. It’s a relationship between peers.
- Self-efficiency. Being able to take actions that will lead you to the change you want to see.
- Self-control. Developing self-control skills.
- Optimism. Reinforcing what you’re doing well.
Based on the results of a review presented by the scientific magazine Nutrition Journal, the authors point out that nutritional coaching is a promising strategy and with a potentially very effective approach to weight loss in the maintenance of both the short-term and long-term behavior, as well as the shift to healthy behavior (Table 2). It is worth noting that this strategy is also interesting in the sense that it has the potential to reduce health care costs (7).
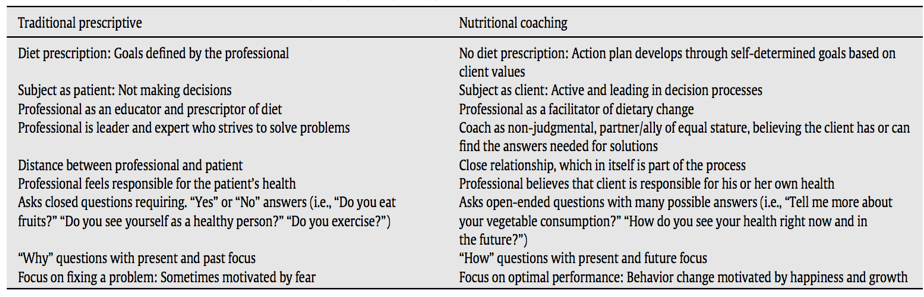
On the other hand, in another systematic review of studies that analyze the coaching process, the authors claim that the nutritional coaching approach is effective for weight loss. More long-term research is needed to provide enough evidence that weight loss results are maintained over time, but no doubt the patient who wants to achieve a nutritional goal needs, in addition to the motivation for change, a recommendation tailored to their needs. Therefore, the best course of action is to design interventions that include dietary-nutritional advice accompanied by strategies based on nutritional coaching in order to achieve success (4).
In any case, not everyone needs nutritional coaching to achieve their nutritional goals, nor does everyone need the motivational reinforcement that coaching entails, so each individual should choose the type of advice that suits their needs and predisposition (5). In short, nutritional coaching is a process that helps you overcome resistance to change. It allows you to become aware of your habits and lifestyle, and to plan the actions that will allow you to achieve the goals you set for yourself, giving you the support you need throughout the process.
Here at Neolife, we’d like to convey that our team of dietitians-nutritionists have received professional training in nutritional coaching and are endorsed by Nutritional Coaching SL, experts in nutritional coaching, in order to accompany you in your process of changing habits and lifestyle. This is the message we always try to remember at Neolife:
“We can’t control how many years we’re going to live, but we can decide how to live them.”
BIBLIOGRAPHY
(1) (2015). The International Association of Coaching. URL: https://certifiedcoach.org/about/
(2) (2017). “Ten facts on obesity”. World Health Organization. URL: https://www.who.int/features/factfiles/obesity/en/
(3) (2003). “Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action”. Geneva: WHO. URL: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42682/9241545992.pdf;jsessionid=4939CAD34A560454DAF38BCE922C0D44?sequence=1
(4) Fleta Y., Giménez J., Meya Molina, A. (2016). “Coaching nutricional para la pérdida de peso” [Nutritional coaching for weight loss]. Hosp. Vol. 33, Nº1, pp: 135-147. URL: https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S0212-16112016000100024
(5) Fleta Y., Giménez J. (2008). “¿Qué es el Coaching Nutricional? ¿Es lo que necesitas?” [What is nutritional coaching? Is it what you need?]. Nutritional Coaching, experts en nutrició. URL: https://nutritionalcoaching.com/blog/coaching-nutricional/que-es-el-coaching-nutricional-es-lo-que-necesitas/
(6) Fleta Y., Giménez J., Meya Molina, A. (2015). “What constitutes Nutritional coaching? Best practices in changing eating habits”. Institute of Coaching. URL: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299031158_What_constitutes_nutritional_coaching_Best_practices_in_changing_eating_habits
(7) Dayan P., Sforzo G. y otros. (2019). “A new clinical perspective: treating obesity with nutritional coaching versus energy-restricted diets”. Nutrition, 60: 147-151. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30586658
